Protocol
![]() EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs protocol is optimized for process data and is transported directly within the standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs protocol is optimized for process data and is transported directly within the standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet![]() Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) frame using Ethertype 0x88a4. It can consist of several sub-datagrams, each serving a particular memory area of the logical process images, that can be up to 4 gigabytes in size. The data sequence is independent of the physical order of the nodes in the network, and addressing can be in any order. Broadcast, multicast and communication between slaves is possible and must be done by the master device. If IP routing is required, the EtherCAT protocol can be inserted into UDP/IP datagrams. This also enables any control with Ethernet protocol stack to address EtherCAT systems.
Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) frame using Ethertype 0x88a4. It can consist of several sub-datagrams, each serving a particular memory area of the logical process images, that can be up to 4 gigabytes in size. The data sequence is independent of the physical order of the nodes in the network, and addressing can be in any order. Broadcast, multicast and communication between slaves is possible and must be done by the master device. If IP routing is required, the EtherCAT protocol can be inserted into UDP/IP datagrams. This also enables any control with Ethernet protocol stack to address EtherCAT systems.
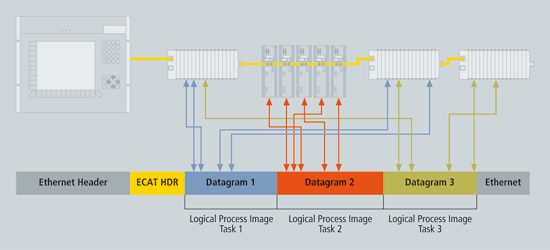
Figure 5-52: Process Data is Inserted in Telegrams
KAS supports CANopen over EtherCAT (CoE). It enables the advantages of EtherCAT in terms of transfer characteristics to be combined with proven, profile-specific drive functions.
KAS also uses File Access over EtherCAT (FoE) protocols to provide options for efficiently exchanging firmware via the bus (see Several Device Profiles and Protocols can coexist).







